Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) businesses, understanding and effectively utilizing financial metrics is crucial for achieving long-term financial success. SaaS finance metrics provide valuable insights into the health and growth of a company, helping decision-makers make informed choices and optimize their financial strategies.
SaaS finances encompass a range of key metrics that help SaaS businesses analyze and measure their financial performance. These metrics enable businesses to track revenue, monitor costs, evaluate cash flow, assess customer acquisition and retention, and gauge overall growth. By leveraging these SaaS finance metrics, companies can make data-driven decisions and drive financial success.
Revenue Metrics
Revenue metrics play a critical role in providing SaaS businesses with a deep understanding of their revenue generation and growth potential.
These metrics provide valuable insights into the financial performance of a company, enabling decision-makers to make informed choices and develop effective strategies to drive revenue growth.
When it comes to SaaS businesses, revenue is typically generated through subscription-based models, where customers pay a recurring fee for access to the software or service. This recurring revenue structure makes it essential to track and analyze revenue metrics to evaluate the health and sustainability of the business.
By examining revenue metrics, SaaS companies can gain a comprehensive view of their revenue streams and identify areas for improvement.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR):
MRR is a critical metric that measures the predictable revenue generated from subscription-based SaaS services on a monthly basis. It includes the revenue from both new and existing customers. Tracking MRR provides visibility into the company’s recurring revenue stream and aids in forecasting future growth.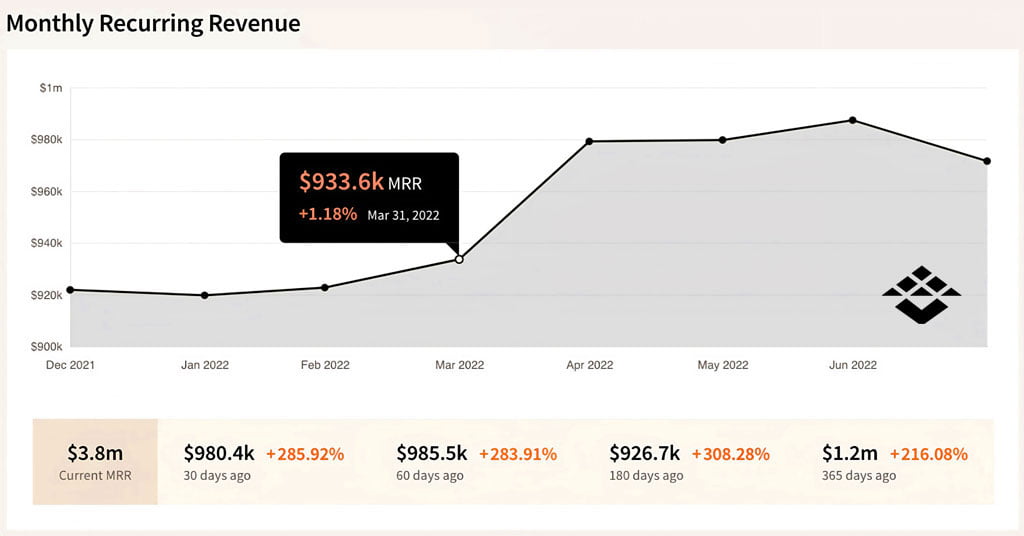
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR):
ARR is the annualized version of MRR, calculated by multiplying the MRR by 12. ARR provides a broader view of the company’s revenue over a longer period, allowing for better strategic planning and performance evaluation. - Average Revenue per User (ARPU):
ARPU is a metric that indicates the average revenue generated per customer. It is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the number of customers. ARPU helps businesses assess the value they are delivering to customers and identify potential upselling or cross-selling opportunities. - Gross Revenue vs Net Revenue:
Gross revenue represents the total revenue generated before accounting for any deductions, while net revenue is the revenue remaining after subtracting costs such as refunds or discounts. Understanding the difference between gross and net revenue is essential for accurately assessing the financial performance of a SaaS business.
Customer Metrics
In the competitive landscape of SaaS businesses, understanding customer behavior and satisfaction is vital for long-term success. Customer metrics play a crucial role in providing insights into customer acquisition, retention, and satisfaction, enabling SaaS companies to build strong and loyal customer relationships.
Customer metrics focus on understanding the various aspects of the customer journey, from initial acquisition to ongoing retention and satisfaction. By tracking and analyzing these metrics, SaaS businesses can make data-driven decisions and develop strategies to enhance customer experience, increase customer loyalty, and drive revenue growth.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC measures the average cost incurred to acquire a new customer. It includes marketing, SaaS sales, and onboarding expenses divided by the number of acquired customers. Tracking CAC helps determine the efficiency of customer acquisition strategies and ensures that the cost of acquiring new customers is justified by their lifetime value.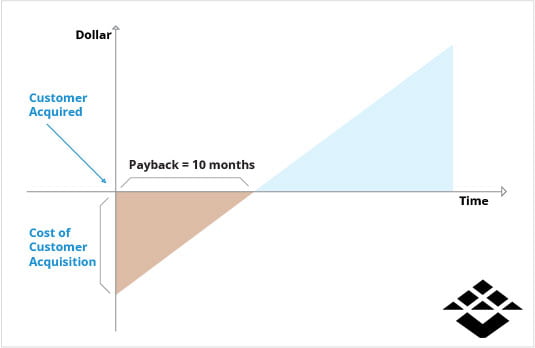
- CAC Payback Period
CAC Payback Period measures the time it takes for a SaaS business to recoup the customer acquisition cost (CAC) through the revenue generated by the acquired customers. It helps assess the financial efficiency of customer acquisition strategies and provides insights into the cash flow dynamics of the business. By monitoring the CAC Payback Period, companies can evaluate the effectiveness of their acquisition investments and optimize their revenue-generating potential. - Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
CLTV is the estimated total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the company. By comparing CLTV with CAC, businesses can evaluate the profitability of their customer acquisition efforts and make data-driven decisions regarding customer segmentation and retention strategies. - Churn Rate
Churn rate quantifies the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions within a given time period. It is a crucial metric as it directly affects revenue and growth. By identifying reasons for customer churn and implementing effective retention strategies, businesses can reduce churn and maintain a stable customer base. - Customer Retention
Customer retention measures the ability of a SaaS business to retain its existing customers over a specified period, which is calculated as the percentage of customers that remain. It is a critical factor in sustaining revenue, ensuring long-term financial success, and assessing the business’s effectiveness in keeping customers engaged with the product or service. - Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer satisfaction and loyalty by gauging customers’ willingness to recommend the product or service to others. It is calculated by surveying customers and asking them to rate, on a scale of 0 to 10, how likely they are to recommend the business to a friend or colleague. Based on their responses, customers are categorized into three groups: promoters (rating 9-10), passives (rating 7-8), and detractors (rating 0-6). The NPS is then determined by subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters.
Cash Flow Metrics
Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business, including SaaS companies. It is crucial to monitor and manage cash flow effectively to ensure the liquidity and financial health of the business. Cash flow metrics provide valuable insights into the movement of cash within a SaaS business, enabling decision-makers to make informed financial decisions and maintain a strong financial position.
Cash flow metrics focus on the inflow and outflow of cash, providing a comprehensive view of a SaaS company’s liquidity. These metrics allow businesses to understand their ability to generate cash from operations, invest in growth opportunities, and meet their financial obligations.
- Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement provides a comprehensive view of a company’s cash inflows and outflows during a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities, enabling businesses to assess their cash position and liquidity. - Free Cash Flow (FCF)
Free cash flow represents the cash generated by a SaaS business after accounting for capital expenditures required to maintain and expand operations. FCF is a key metric for assessing the company’s ability to generate cash and invest in growth opportunities. - Runway
Runway refers to the amount of time a company can sustain its operations with its available cash resources. It is calculated by dividing the cash balance by the average monthly burn rate. Monitoring the runway helps businesses plan for future funding needs and make strategic decisions. - Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
CCC measures the time it takes for a SaaS business to convert its investments in resources and services into cash inflows from customers. Unlike traditional businesses that deal with physical inventory, SaaS businesses focus on optimizing the CCC by considering factors such as the average time for accounts receivable collection and accounts payable payment.For SaaS businesses, the CCC primarily revolves around managing the time it takes to collect payments from customers (accounts receivable) and the time taken to settle payments to suppliers and service providers (accounts payable). By efficiently managing these processes, SaaS companies can improve their cash flow and operational efficiency.
Growth Metrics
Growth is a fundamental objective for any SaaS business. To thrive in a competitive market, SaaS companies must continuously expand their customer base, increase revenue streams, and scale their operations. Growth metrics play a pivotal role in measuring and evaluating the expansion and scalability of a SaaS business, providing valuable insights to drive strategic decision-making.
Growth metrics reflect the overall performance and progress of a SaaS company, serving as key indicators of its ability to achieve sustainable growth and stay ahead of the competition. These metrics help businesses track their progress over time, set growth targets, and assess the effectiveness of their growth strategies.
- Annual Growth Rate (AGR)
AGR measures the percentage increase in revenue over a year. It provides insights into the company’s growth trajectory and overall performance. - Month over Month Growth Rate (MoM)
MoM growth rate measures the percentage increase in revenue or other key metrics on a month-to-month basis. It helps track short-term growth trends and identify any anomalies or patterns. - Year over Year Growth Rate (YoY)
YoY growth rate compares the revenue or other key metrics of the current year to the same period in the previous year. It provides a more comprehensive view of growth over a longer time frame. - Customer Growth Rate
Customer growth rate measures the percentage increase in the total number of customers over a specific period. It indicates the company’s ability to attract and onboard new customers while also considering the retention of existing customers. It reflects the overall growth in the customer base, encompassing both new customer acquisitions and customer retention efforts. - SaaS Magic Number
The SaaS Magic Number is a growth metric specifically designed for SaaS businesses. It calculates the efficiency of a company’s sales and marketing investments in acquiring new customers. The formula typically involves dividing the incremental revenue generated by the company in a specific period by the total sales and marketing expenses incurred during that period. A higher SaaS Magic Number indicates a more efficient and scalable customer acquisition strategy.
How to Use SaaS Finance Metrics for Financial Success
- Set clear financial goals
Define specific financial objectives aligned with your business strategy and use finance metrics to measure progress and success. - Regularly monitor and analyze metrics
Establish a process to collect, analyze, and review finance metrics on a regular basis. This will help identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. - Benchmark against industry standards
Compare your finance metrics with industry benchmarks to assess your company’s performance and identify areas where you can excel or need improvement. - Identify areas for optimization
Use finance metrics to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas of high costs. This will enable you to optimize your operations, reduce costs, and improve profitability. - Develop data-driven strategies
Leverage finance metrics to inform your decision-making process. Use the insights gained from these metrics to develop data-driven strategies for customer acquisition, retention, pricing, and cost management. - Foster cross-functional collaboration
Finance metrics should not be limited to the finance department. Encourage collaboration between finance, marketing, sales, and customer success teams to ensure alignment and shared accountability for financial success. - Adapt and iterate
Continuously review and adapt your financial strategies
Conclusion
Understanding and tracking important SaaS metrics is essential for driving financial success in the dynamic world of SaaS businesses. These metrics provide valuable insights into revenue generation, customer acquisition and retention, cost management, cash flow, and growth.
In today’s competitive landscape, continuous learning and knowledge, for example in SaaS product management and B2B SaaS sales process are crucial for SaaS startups and entrepreneurs. By expanding their expertise through SaaS courses or classes, SaaS leaders gain valuable insights and effective strategies for maximizing their revenue growth potential and ensuring long-term success. And by focusing on tracking and monitoring key metrics for SaaS such as customer acquisition and retention, revenue generation, and cost management, SaaS startups can fine-tune their strategies and allocate resources effectively. This data-driven approach empowers them to optimize their financial performance and navigate the challenges of being a startup in the competitive SaaS industry.
FAQs
What is the difference between gross revenue and net revenue?
Gross revenue is the total revenue before deducting expenses, while net revenue is the revenue remaining after subtracting costs like COGS and operating expenses. Net revenue reflects the actual revenue contributing to profitability.
How do I calculate my churn rate?
Churn rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers lost in a specific period by the total number of customers at the beginning of that period. Multiply the result by 100 to get the churn rate as a percentage.
How do I determine my customer acquisition cost?
Calculate customer acquisition cost (CAC) by dividing total marketing, sales, and onboarding sales expenses in a specific period by the number of customers acquired in that period. CAC helps evaluate the effectiveness of customer acquisition efforts.
What is a healthy operating expense ratio?
A healthy operating expense ratio is lower than industry averages or benchmarks. It is calculated by dividing operating expenses (excluding COGS) by net revenue and multiplying by 100. Control and monitor operating expenses to optimize profitability.
How do I calculate my free cash flow?
Calculate free cash flow (FCF) by subtracting capital expenditures from operating cash flow. Operating cash flow represents cash generated from regular operations. FCF indicates available cash for reinvestment, debt reduction, or shareholder distribution.

